Project planning tools are essential for effective project management, regardless of size or complexity. This guide delves into the core functionalities, various types, and best practices for utilizing these tools to enhance project success. We will explore different approaches, from Gantt charts to Kanban boards and agile methodologies, examining their strengths and weaknesses across diverse project contexts.
Understanding how to select, implement, and integrate these tools is crucial for optimizing workflows and achieving project objectives.
The selection process itself involves careful consideration of project specifics, team dynamics, and budgetary constraints. This guide will equip readers with the knowledge to make informed decisions, ultimately leading to the choice of a project planning tool that perfectly aligns with their unique needs.
We’ll also cover effective data visualization techniques to ensure clear communication and progress tracking throughout the project lifecycle.
Using Project Planning Tools Effectively
Project planning tools are indispensable for successful project management. They provide a visual framework for organizing tasks, allocating resources, and tracking progress, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and on-time project completion. Effective utilization hinges on understanding the strengths of each tool and applying best practices for collaboration and progress monitoring.
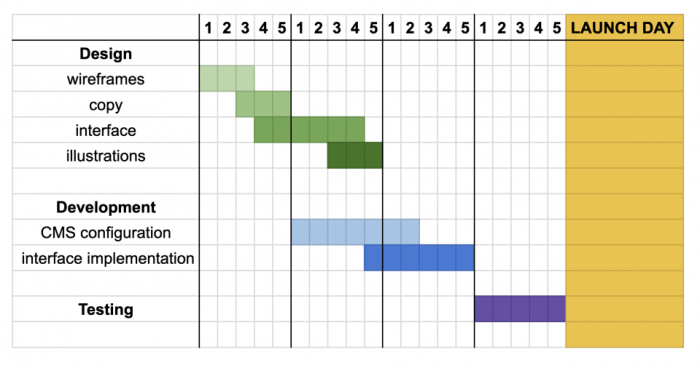
Gantt Chart for Project Scheduling
A Gantt chart offers a visual representation of a project schedule, displaying tasks as horizontal bars plotted against a timeline. The length of each bar corresponds to the task’s duration, and dependencies between tasks are clearly shown through the bar placement.
This allows for a quick overview of the project’s timeline, identification of potential bottlenecks, and easy assessment of task progress. For example, a software development project might use a Gantt chart to illustrate the sequential dependencies between design, coding, testing, and deployment phases, visually highlighting critical path activities and potential delays.
The chart’s clear visual structure allows for quick identification of potential scheduling conflicts and facilitates proactive adjustments.
Kanban Board for Task Management
A Kanban board is a visual workflow management system that uses cards to represent tasks. These cards are moved across columns representing different stages of the workflow, such as “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.” This provides a real-time view of the project’s status and allows for easy identification of bottlenecks and task prioritization.
Imagine a marketing team using a Kanban board to manage the launch of a new product. Each task, from content creation to social media scheduling, would be represented by a card, allowing the team to monitor progress and identify any tasks that are falling behind schedule.
The visual nature of the board facilitates quick identification of work-in-progress and aids in efficient task assignment and re-prioritization.
Best Practices for Enhancing Team Collaboration
Effective project planning tools facilitate team collaboration by providing a centralized platform for information sharing and task assignment. Regular updates, clear communication channels integrated within the tool, and shared access to project documents foster transparency and accountability. For instance, a project management tool with integrated communication features allows team members to discuss tasks, share files, and provide updates directly within the project workspace, minimizing email clutter and improving response times.
This shared workspace promotes a collaborative environment and reduces the risk of miscommunication or duplicated efforts. Using features like task assignments and progress tracking helps everyone stay informed and accountable.
Tracking Project Progress and Milestones
Utilizing project planning tools for progress tracking involves setting clear milestones and regularly updating the project status. Tools often provide features like progress bars, dashboards, and reporting capabilities that visualize project performance against the planned schedule. For example, a construction project might utilize a project management tool to track the completion of various phases, such as foundation work, framing, and finishing.
The tool could generate reports showing the percentage completion of each phase, highlighting any delays and enabling proactive mitigation strategies. Regular updates ensure that the project stays on track and allows for early identification and resolution of any potential issues.
Project Planning Tool Integrations
Harnessing the power of interconnected systems is key to optimizing project management. Integrating your project planning tool with other software applications can significantly streamline workflows, improve communication, and enhance overall project efficiency. This integration fosters a dynamic ecosystem where data flows seamlessly, eliminating manual data entry and reducing the risk of errors.Integrating project planning tools with other software offers a multitude of advantages.
By connecting these systems, project managers gain access to a holistic view of their projects, encompassing not just tasks and timelines, but also customer information, communication threads, and resource allocation. This integrated approach reduces data silos and fosters a more informed decision-making process.
Benefits of Integration, Project planning tool
The benefits of integrating a project planning tool are multifaceted and lead to a more efficient and productive project environment. Improved data visibility, reduced redundancy, and enhanced collaboration are just a few key advantages.
- Enhanced Data Visibility:A centralized system provides a single source of truth, allowing all stakeholders access to the most up-to-date project information. This eliminates the confusion caused by disparate data sources and ensures everyone is on the same page.
- Reduced Redundancy:Integrating systems minimizes duplicate data entry, saving time and reducing the potential for human error. Information is automatically updated across platforms, streamlining the workflow and freeing up valuable time for more strategic tasks.
- Improved Collaboration:Seamless integration facilitates real-time communication and collaboration. Team members can access relevant project information and communicate directly within the integrated platform, fostering a more cohesive and productive team environment. For example, a change in project scope reflected in the planning tool could automatically trigger a notification in the communication platform, keeping everyone informed.
- Streamlined Reporting:Integrated systems simplify the process of generating comprehensive project reports. Data from various sources can be automatically compiled, providing a clear and concise overview of project progress, resource utilization, and key performance indicators.
Challenges of Integration
While the benefits of integration are substantial, it’s crucial to acknowledge the potential challenges. Careful planning and execution are essential to ensure a successful integration process.
- Data Migration:Transferring data from existing systems to the integrated platform can be a complex and time-consuming process. Data cleansing and validation are crucial to ensure data integrity and accuracy.
- Compatibility Issues:Different software systems may have varying data formats and APIs, leading to compatibility challenges. Careful consideration of system compatibility is crucial before initiating the integration process.
- Cost and Resources:Integrating different software systems requires investment in both time and resources. This includes the cost of software licenses, integration services, and internal staff time.
- Security Concerns:Integrating multiple systems can introduce security risks if not properly managed. Robust security measures are essential to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
Workflow Diagram: Project Planning Tool and Communication Platform Integration
Imagine a workflow diagram depicting a simplified integration between a project management tool (e.g., Asana) and a communication platform (e.g., Slack). The diagram would visually represent the flow of information. A new task created in Asana, for instance, would automatically generate a message in a designated Slack channel, notifying the team.
Similarly, a comment or update within Slack could be linked or mirrored in the Asana task, maintaining a single source of truth and ensuring consistent information across both platforms. The diagram would use clear visual elements like boxes representing each system and arrows indicating the direction of data flow.
Key actions, like task creation, updates, and notifications, would be clearly labeled. The overall visual would emphasize the seamless flow of information between the two systems, highlighting the efficiency gained through integration.
Visualizing Project Data
Project planning tools go beyond simple task lists; they empower teams to visualize project data in compelling ways, fostering better understanding, improved communication, and ultimately, successful project delivery. By transforming raw data into insightful visuals, these tools allow stakeholders to quickly grasp project progress, identify potential roadblocks, and make data-driven decisions.Effective visualization translates complex project information into easily digestible formats, reducing ambiguity and promoting shared understanding across teams.
This not only improves efficiency but also strengthens collaboration and accountability. The ability to see the project’s health at a glance is invaluable, especially in larger, more complex projects.
Project Timeline Visualization
A compelling visual representation of a project timeline typically uses a Gantt chart. Imagine a horizontal bar chart where each bar represents a task, its length corresponding to the task’s duration. The chart’s horizontal axis displays the project’s timeframe, while the vertical axis lists the tasks.
Milestones are visually highlighted, perhaps with differently colored diamonds or flags, marking key achievements or decision points. Dependencies between tasks are shown with connecting arrows, illustrating the sequential order of activities. The overall visual provides a clear, at-a-glance view of the project’s schedule, highlighting critical paths and potential bottlenecks.
For instance, a red bar extending beyond the project’s deadline immediately flags a task requiring attention.
Communicating Project Status with Visual Elements
Project planning tools offer various ways to communicate project status visually. Progress bars, for example, instantly convey the completion percentage of individual tasks or the overall project. Color-coding can further enhance this, with green representing completed tasks, yellow indicating tasks in progress, and red signaling tasks behind schedule.
Burn-down charts offer a dynamic view of the remaining work, plotting the amount of work left to do against time. A consistently downward sloping line indicates the project is on track; a flattening or upward trending line suggests potential delays.
These visual cues, coupled with concise text summaries, provide a comprehensive yet easily understandable project status report. A dashboard consolidating multiple such visualizations provides a single, powerful overview of the project’s health. For example, a dashboard might show a Gantt chart alongside progress bars for each phase, a burn-down chart, and a risk register, all updated in real-time.
Ending Remarks
Effective project management hinges on the strategic selection and skillful application of appropriate planning tools. This guide has provided a framework for understanding the diverse landscape of project planning tools, from their core functionalities to advanced integration capabilities. By mastering the techniques and best practices Artikeld, project managers can significantly improve their ability to plan, execute, and monitor projects, leading to enhanced efficiency, reduced risks, and ultimately, successful project outcomes.
The ability to visualize data and communicate progress effectively further solidifies the importance of utilizing these powerful tools.
